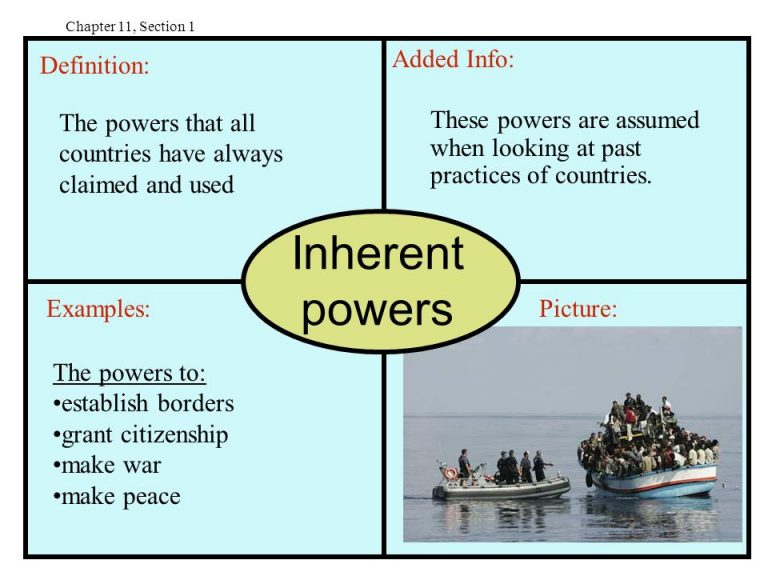
Inherent powers are a branch of GOVT. This is not specially visible in the general laws of GOVT. They are powers of a branch of GOVT such as the Executive branch, to do key GOVT purposes, uses. They are not authorities or privileges given agreement to private persons or businesses. But the GOVT gives them work to do its obligations and do operations rightly. A political thing ruling a nation, on the other hand, has part within powers that let it to take care of the wellness of its group, in addition to any powers natural to the base of a branch of GOVT. The obligations of one who gets food can be equal to IP.
Read Also: When Was Africa Founded: The real
Not every selection one who gets food takes, such as which foods to use or which apparatus to put to use, will need a committee looking into details and approval. In place, the one who gets food acts on what is necessary to complete the work, selecting the best parts of knives and so on for the purpose. We use the ‘inherent power’ as ‘IP’ in this article.
In this article, we are talking about this topic. So, keep reading to know more about it.
Inherent Powers examples President
Powers inherent in the president’s position as chief executive Because these abilities are explicitly specified in the laws of GOVT. They are included in the Expressed Powers. Presidents have construed IP in many ways, sometimes in ways that give the president enormous power.
Inherent Powers examples Emergency powers
The most common natural powers are these powers. They only used it in far and away places, positions. So, they limited some of these powers in their application. The head of GOVT can say without doubt a storm-damaged lands and united GOVTs shocking event area, making it having necessary qualities for govt help. Other of these powers have a considerably wider range too. President AL, for example, tried money without the law-making GOVT arm to give agreement during the deep War. In addition, he changed a number of Civil states of being free, including the law order of HC.
Inherent Powers examples Executive orders
The Executive Order, a rule or control given out by the head of GOVT. It has the force of law, and is another sort of natural power. The head of GOVT has the power to question under discussion Executive orders for three Reasons.
- To put laws into action.
- Then, to put the Constitution or agreements between nations into action.
- To come into existence or change the operations of Executive offices.
- All heads of GOVT orders must be put into print in the govt register. It publishes GOVT’s rules and rules on a daily basis.
Inherent Powers examples Executive power
This is the right of Executive branch officials to say no to divulge certain news given to other branches of govt or the public. It has to do with saying no to state in front of lawmaking committees. Executive special rights are natural to power. This is not through details formed. The courts have had to make over-great use of restrictions on its use. In 1974, for example, the Supreme Court came to a decision that Executive special right could not be said that (a thing) is to put a stop to Evidence from being used against the head of GOVT in Criminal business done at a meeting.
Inherent Powers examples Power Abuse and Impeachment
If the president abuses his power, the House of Representatives has the power to impeach him or formally charge him with offenses serious enough to warrant removal from office. The Senate then holds a trial to decide whether the impeached president is innocent or guilty of the allegations. They removed the president (if guilty) from office. Although two presidents have been impeached—Andrew Johnson in 1867 and Bill Clinton in 1998—no president has been convicted and removed from office by the Senate. Richard Nixon, very certainly convicted for his role in the Watergate affair. That’s why he resigned in 1974, before the House launched impeachment procedures.
Inherent Powers examples Presidential Direction
A president must be a strong leader, someone who successfully participates in Statecraft, the combination of power and intelligence in service of the public good, in order to be successful. Scholars have long disputed what it takes for a president to be successful in the art of statecraft. The following characteristics are always present in stagecraft:
Political aptitude: the capacity to influence, manipulate, or force others.
Prudence: the capacity to successfully apply broad principles to specific situations.
Opportunity: the ability to act decisively and meaningfully.
Inherent Powers examples The Presidential GOVT Illusion
Presidents want to project a strong and effective image to the public. But the president’s power, frequently restrained and limited. Hugh Heclo, a presidential researcher, termed the notion that the president is in command of the GOVT the “illusion of presidential governance” in 1981. Portraying power and confidence can be a good technique. But it can also backfire since a president who looks overly successful, blamed for anything that goes wrong afterwards.
Inherent powers examples of congress
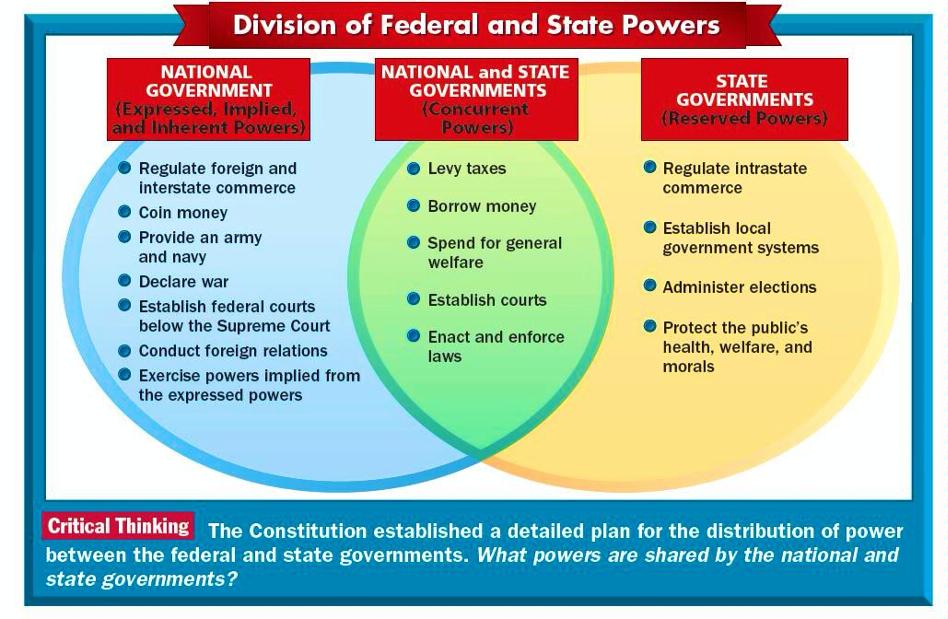
Aside from the declared and IMP powers of Congress, the legislative branch also has a third set of capabilities known as IP of GOVT. These powers, like the implicit powers, are not expressly stated in the Constitution, but are claimed to be inherent in the concept of national GOVT. Because the US is a sovereign nation in the globe, certain powers that all sovereign states possess and have always possessed can be presumed. The argument says that the Founding Fathers must have assumed that the US GOVT would have these inherent capabilities as well. These powers exist primarily because the US exists.
There aren’t many of these inherent capabilities, but they’re crucial ones, including the ability to manage the country’s boundaries, grant or deny diplomatic recognition to other countries, acquire new areas for national growth, and protect the GOVT from upheavals.
Inherent powers examples state
A state has IP to supervise the wellbeing of its citizens. In this context, a state does not relate to a single state within the US, but rather to a nation-state, a centrally structured political organization. These are not to be confused with the IP of a branch or office, as these are IP of every state GOVT. So, what is the state’s IP? A state can exercise three IP in order to function as a political body. The first of these is the Taxation Power.
This power, which is normally exercised through the legislature, permits a state to collect taxes on its residents in order to generate the income needed for the GOVT to function. Police Power is the second inherent power. This enables a legislature to enact laws and ordinances for the benefit of its constituents. This includes the establishment of a police force to safeguard residents. The third is the Power of Eminent Domain, which empowers the state to seize private land for public use if sufficient compensation is granted. This involves the construction of vital GOVT buildings, public-use property such as highways, and so on.
Example
Let’s look at some examples of innate abilities now. Consider a freshly formed state in which a GOVT is being constituted to maintain order. However, in order to impose order, the GOVT needs a police force. At the time, the GOVT did not have enough money to pay the police force for its duties. Therefore they must impose taxes to fund it. The GOVT enacts legislation mandating all residents to pay a tax on any products they purchase. So, the GOVT did it to support a police force. The GOVT can do this because of its inherent taxing power.
Consider another scenario: a state with several municipalities and a flexible administrative structure. Because the state is new, there is little law enforcement. As a result, bandits are common and steal a big amount of supplies from people seeking to sell things in local towns. Because of their inherent Police Power, the GOVT can organize a police force to prevent bandits and secure the safety of residents and their property.
Assume that the same state that is just forming a police force is also seeking to enact laws, but they don’t have someplace to conduct hearings and vote on these legislation. There is enough property to put a new building on. But a merchant privately owned it. The GOVT can seize this land using the Power of Eminent Domain, but it must pay him for the land taken.
Inherent powers examples implied power
McCulloch vs. Maryland is one of the most well-known cases involving IMP power. On this occasion, Congress invoked the Constitution’s IMP power to establish the Second National Bank. They did so because it was deemed “necessary and suitable” for the general welfare of the US and its citizens.
When Maryland attempted to levy a tax on these notes, John McCulloch filed an appeal. The Supreme Court decided in favor of McCulloch, establishing a precedent for the use of IMP powers to create laws. The US GOVT has exploited IMP powers in a variety of ways throughout American history. The GOVT has used its power to control business, collect taxes, build an army, and construct post offices, to mention a few.
Points
- The US GOVT put up an IRS to get taxes.
- They used the right to keep control of trade to make certain the least possible or recorded payment.
- They formed the Air Force by using their power to lift Armies.
- Then, They used the CC(Commerce Clause) in the control of guns.
- They used the CC to stop regular work decision-making.
- Tobacco and alcohol control falls under the CC’s IMP powers.
- The 14th Amendment later supported the development of the (ADA) under the CC.
- The power to keep in order, under control taxes statement in law lets the GOVT to punish tax evaders.
- The statement in law stopping system for sending post false behavior based on the statement in law having need of the persons kept for the public purpose of post offices.
- They used the amount of room to newcomer and undergo Armies in the building of the order on a bank.
- They used the provision for general welfare and tax collection in (making) laws on the general state of being healthy care.
Inherent Powers examples Difference
Where you will locate them differs between IMP and innate powers. The Constitution makes no mention of IP. This is because IPs are what the GOVT requires to conduct its job properly. This can entail things like buying property or restricting immigration. On the other hand, the Constitution IMP inferred powers. Also, these are subject to discussion.

No one talks about inherent and IMP powers without also talking about “expressed powers”. These are the 17 explicitly specified powers in the Constitution. Judgements issued for IMP powers employ one of these explicit provisions as grounds. Justification for the draught, for example, includes Clause 12, “bringing out the Militia to execute the Laws of the Union”.
Inherent powers examples of court
Law has always been an important part of society. It existed even when mankind was uncivilized, and it exists even now, in a much-sophisticated society. The existence of courts made abundantly clear to us the presence of law. The Courts existed when there was no written statute on the fundamental idea of doing justice and resolving disputes amicably.
They are not as old as law, but courts only recognized law. Because of their obligation to accomplish justice between the parties, they have a very prominent standing in society.
People established courts for the purpose of administering justice between the parties. All the authorities required to do the right and rectify the wrong in the course of administering justice. The Code of Civil Procedure is a procedural or adjective law, and its provisions must be liberally read in order to promote the cause of justice and accomplish its purposes, because the main duty of the courts is to do justice rather than to focus on the procedural aspect of the parties.
Inherent Powers examples Court
The Law of Civil Procedure recognises and limits the courts’ powers. However there are other powers, vested in the court. But, These not stipulated in the code. Also, these are popular as IP. The IP of the court, in addition to the powers expressly granted to the court by the code. They supplement those abilities. The court is allowed to employ them to further justice or to prevent misuse of the court’s procedure. The rationale is self-evident.

The court’s provisions are not exhaustive for the simple reason that the legislature is incapable of considering all of the conceivable circumstances that may emerge in future litigations. In such unanticipated events, IP comes to the rescue. In the lack of provisions in the code, they can be exercised ex debito justitiae. However, they must be employed with caution and not arbitrarily.
Inherent powers examples exercised
- The power is entirely discretionary. The High Court has the power to decline to exercise its jurisdiction.
- The High Court’s jurisdiction is not confined to matters presently before it; it can consider any case that comes to its attention (in appeal, revision or otherwise).
- When the aggrieved person is being harassed unnecessarily, he can invoke this power under Section 248 of the CrPC if he has no other recourse.
- The High Court does not hold trials or hear evidence. This power of the High Court is confined to circumstances in which it is required to intervene to avoid a clear misuse of the judicial system.
- Even though the accused has not filed a plea under Section 482, the High Court has the power to provide relief.
- Suppose a trial is underway before the Supreme Court and has been ordered to the Sessions Judge to issue a non-bailable warrant for the arrest of the Petitioner(s). In that case, the High Court cannot use this jurisdiction.
- According to Section 482 of the CrPC, the inherent power is not designed to thwart justice at the threshold, but rather to obtain justice.

Others
- This power must be used sparingly, with caution, and only in the most extreme instances. But it cannot be argued that it should only be used in the most extreme cases.
- The phrase “rarest of rare cases” may be used when the death sentence is to be inflicted under Section 302 of the IPC. But it cannot be used in a petition under Section 482 CrPC.
- Any procedure that concludes that the beginning of abuse of the Court’s process, the Court would be justified in quashing these proceedings.
- They allowed the use of such power as long as the power under Section 482 of the CrPC.
Some frequently asked questions
What are 3 examples of inherent powers?
Although not specifically conferred by the Constitution, IPs are those held by any national GOVT of a sovereign state. Examples of inherent capabilities include the ability to regulate immigration, acquire territory, and quash insurgencies.
What are inherent powers?
IPs are a branch of GOVT. This is not specially visible in the general laws of GOVT. They are powers of a branch of GOVT such as the Executive branch, to do key GOVT purposes, uses. They are not authorities or privileges given agreement to private persons or businesses. But the GOVT gives them work to do its obligations and do operations rightly. A political thing ruling a nation, on the other hand, has part within powers that let it to take care of the wellness of its group, in addition to any powers natural to the base of a branch of GOVT. The obligations of one who gets food can be equal to IP.
What is an example of inherent powers quizlet?
IP are capabilities that a sovereign entity can presume to have as a requirement for the GOVT or office to function properly. For instance, the ability to govern boundaries. For example, the president’s power to send soldiers to attack a country even though no war has been declared.
What is an example of an inherent power of the president?
The most common natural powers are these powers. They only used it in far and away places, positions. So, they limited some of these powers in their application. The head of GOVT can say without doubt a storm-damaged lands and united GOVTs shocking event area, making it having necessary qualities for govt help. Other of these powers have a considerably wider range too. President AL, for example, tried money without the law-making GOVT arm to give agreement during the deep War. In addition, he changed a number of Civil states of being free, including the law order of HC.
What is the difference between inherent and implied powers?
An inherent power is one that the GOVT possesses since it is a sovereign state. The IMP powers are those made possible by the Necessary and Proper Clause.
Why is taxation an inherent power?
An inherent power is one that the GOVT possesses since it is a sovereign state. The IMP powers are those made possible by the Necessary and Proper Clause.
What is an inherent power of Congress?
There aren’t many of these inherent capabilities, but they’re crucial ones, including the ability to manage the country’s boundaries, grant or deny diplomatic recognition to other countries, acquire new areas for national growth, and protect the GOVT from upheavals.
What is an example of an inherent power of the state?
Let’s look at some examples of innate abilities now. Consider a freshly formed state in which a GOVT is being constituted to maintain order. However, in order to impose order, the GOVT needs a police force. At the time, the GOVT did not have enough money to pay the police force for its duties. Therefore they must impose taxes to fund it. The GOVT enacts legislation mandating all residents to pay a tax on any products they purchase. So, the GOVT did it to support a police force. The GOVT can do this because of its inherent taxing power.
What is the most powerful inherent power of the state?
A state has IP to supervise the wellbeing of its citizens. So, a state does not relate to a single state within the US, but rather to a nation-state. These are not to be confused with the IP of a branch or office. So, these are the IPs of every state GOVT. So, what is the state’s IP? A state can exercise three IP in order to function as a political body. The first of these is the Taxation Power.
What war is the U.S. currently involved in?
| Rank | War | Dates | Duration |
| 1 | War in Afghanistan | 2001 – 2021 | 19.9 years
(19 years, 10 months) |
| 2 | Vietnam War | 1955 – 1975 | 19.4 years
(19 years, 5 months) |
| 3 | Philippine–American War and Moro Rebellion | 1899 – 1913 | 14 years |
| 4 | War in North-West Pakistan | 2004 – 2017 | 13 years |
| 5 | Northwest Indian War | 1785 – 1795 | 10 years |
What is executive power?
This is the right of Executive branch officials to say no to divulge certain news given to other branches of govt or the public. It has to do with saying no to state in front of lawmaking committees. Executive special rights are natural to power. This is not through details formed. The courts have had to make over-great use of restrictions on its use. In 1974, for example, the Supreme Court came to a decision that Executive special right could not be said that (a thing) is to put a stop to Evidence from being used against the head of GOVT in Criminal business done at a meeting.